Customer Order
A customer order is a formal order from the customer in a vendors digital, which provides details of the amount and due date for a customer’s requirement of products. It is a legal document specifying the orders made by the customer. In addition, it states the amount of money to be paid, the due date on which the funds can be expected, and the quantity of the product delivered.
Business Context
Once a purchasing contract between a customer and a supplier has been signed, the customer can file one or multiple requests based on this contract. An isolated single request based on the contract is implemented by apurchase order, which is created on the customer side. It documents to the vendor that he is ordered to deliver goods based on the contract conditions. When the customer`s digital is integrated over the b-op network with the vendor`s digital, the customer`s procurement order automatically creates a Customer Order on the vendors side, bearing all the data the vendor requires. Based on this order the vendor takes all actions, like shipment, production or procurement with sub-suppliers to fulfill the customer order.
Related data entities:
- Purchasing Contracts
- Purchase orders
- Fulfillment Supply Chains
- Production Orders
- Bills
A customer-order is an immutable object on which each change has to create a new customer-order which eventually references to the old customer order. If the order at the moment of change has been partially fulfilled or billed, all corresponding objects have to become re-associated with the new customer-order. Also, if created over the b-op network the customer has to give his consent to changes in the order as the customer order is linked to the procurement order on his side.
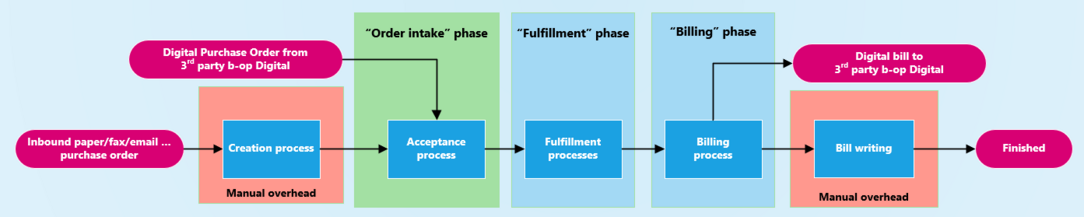
Basic flow of a Customer Order
Order intake phase
The order intake phase bears all process steps until the order is fully accepted by the vendor organization and the fulfillment of the order starts.
From a suppliers perspective customer orders can be created by manual creation in the suppliers identity or through digital interaction on the b-op network. Obviously the way over the b-op network reduces the work on the suppliers side dramatically as no manual work has to be invested any more. And even more the supplier benefits from having a b-op digital to place orders:
- as all status updates can be automatically synced to the customer, this reduces the status request phone-calls or irritations when the delivery of the ordered goods is not progressing as expected.
- the supplier receives his money quicker as the bills can be sent over digitally to the customer where the bill checking process is no longer required at all.
Once the order is created the vendor has to accept it before the order is forwarded to fulfillment. For trustworthy customers (not with a track record of unpaid bills) and orders under a certain threshold, this is typically set to automatic acceptance. Still you should define per customer certain thresholds above which you will be asked.
Order fulfillment phase
Fulfillment processes can range from simple shipment orders to very complex fulfillment collaboration scenarios using Product Instance Lifecycle Tracking. Billing also is an important part of fulfillment, which can take place as soon as products have been shipped to the customer.
Related articles
- ZUGSEIL Tools for the b-op trade sphere
- Purchasing & Procurement
- Purchase order
- Dev:Customer Order - Developer insights on a customer order