Regular stocktaking
Revision as of 23:07, 18 November 2023 by Stefanseiler (talk | contribs)
Regular stocktaking is a crucial process for businesses that involves systematically counting and recording the quantity of inventory or goods held in stock. The primary purpose of stocktaking is to ensure accurate and up-to-date records of inventory levels, which helps in managing stock efficiently, preventing stockouts or overstock situations, and identifying potential discrepancies or theft.
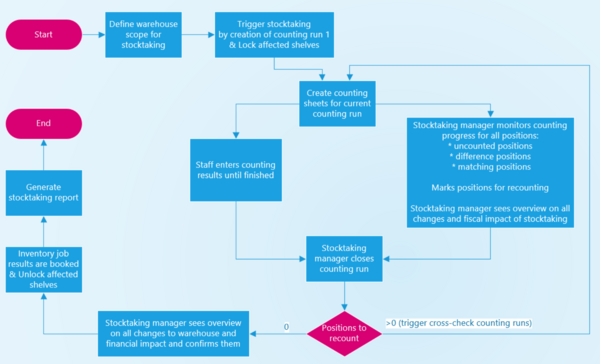
Here is a step-by-step explanation of a typical regular stocktaking process:
- Planning:
- Determine the frequency of stocktaking: This could be done monthly, quarterly, or annually, depending on the nature of the business.
- Schedule a time: Choose a time that minimizes disruption to normal business operations. Often, stocktaking is conducted during off-peak hours or weekends.
- Assemble a team: Select a team of trained individuals responsible for conducting the stocktake. The team size and composition depend on the size and complexity of the inventory.
- Counting:
- Conduct physical counts: The team physically counts the items in stock. This can be done by counting individual units, measuring bulk quantities, or using technology like barcode scanners for faster and more accurate counts.
- Record counts: Document the counts on count sheets or input them directly into the inventory management system.
- Verification:
- Cross-check counts: Compare the physical counts with the recorded quantities in the system. Investigate and resolve any discrepancies.
- Identify and address issues: If there are discrepancies, investigate the root causes. It could be errors in recording, theft, or other issues that need to be addressed.
- Reconciliation:
- Adjust inventory records: Update the inventory records based on the verified physical counts. This step is critical for maintaining accurate stock levels.
- Analyze results: Evaluate the stocktake results to identify trends, areas for improvement, and potential adjustments to inventory management practices.
- Reporting:
- Generate reports: Create reports summarizing the stocktake results, including any discrepancies, adjustments, and recommendations for improvement.
- Communicate findings: Share the stocktake results with relevant stakeholders, such as management, finance, and operations teams.
By regularly conducting stocktakes, businesses can maintain control over their inventory, reduce the risk of errors, and ensure accurate financial reporting.